Watch the recorded lesson HERE
Read: The Object of Rotary is to encourage and foster the ideal of service. Each person’s occupation is an opportunity to serve society. Vocational service means helping others through their profession. Rotary clubs include men and women from diverse professions. The name “Rotary” came from the practice of rotating meeting sites among members’ places of business. Rotary recognizes the importance of all occupations. Rotarians serve others by using their skills to help others discover new professional opportunities and interests.
Discuss: How have you or someone you know used their profession to serve others?
UNDERSTANDING VARIABLE COSTS AND FIXED COSTS
Watch: Careful With Fixed Costs (below)
Read: There are two types of expenses in running a business: variable costs and fixed costs.
Variable Costs: The price of some things a business needs will change depending on how much they make and sell. These things are called “variable costs”. Some common examples of variable costs are the work needed to make and sell a product, the ingredients needed to make the product, or shipping the product to customers.
Fixed Costs: Some things a business needs will stay the same no matter how much they make and sell. These are called “fixed costs”. Examples of fixed costs are rent for a place to do business, paying back loans, paying workers, paying for things like electricity and water, and making sure the business is protected by insurance. Business owners should be careful before they start paying for new fixed costs.
Example: Daniel owns a woodworking shop where he makes chairs, tables and furniture for his customers. Look at Daniel’s business expenses. He circled fixed or variable to show which type of expenses he has:
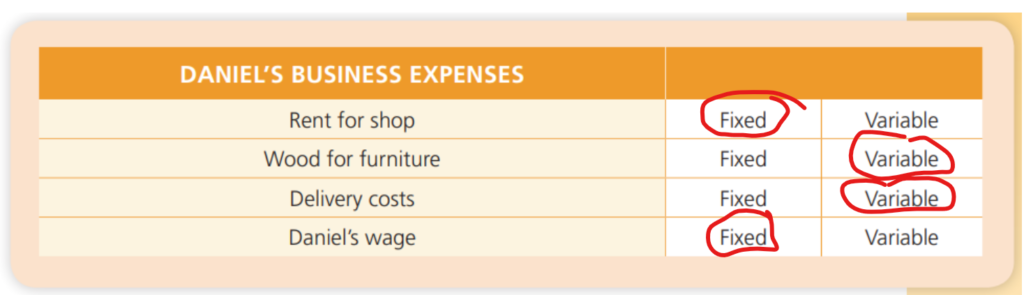
What business expenses are required for your business? List each expense below. Tell if it is a Fixed Cost (stays the same no matter how much you make and sell) or a Variable Cost (changes depending on how much you make and sell). Then type the amount of each expense converted into US dollars so your sponsor can understand.
UNDERSTANDING NET PROFIT MARGIN
Read: Profit is the money a business keeps after the costs (often called expenses) are taken away from the sales revenue.
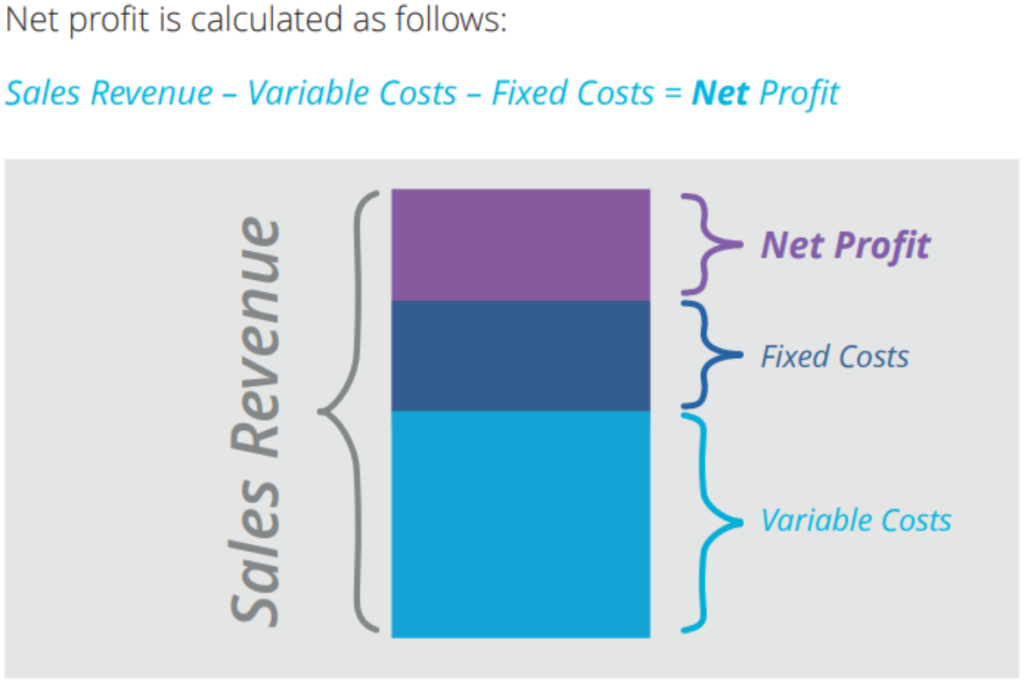
To know if your business is succeeding, you need to know the profit margin. The profit margin is a percentage that you can calculate using math. This percentage tells you about the profitability of your business.
Video: How to Calculate Net Profit Margin
Read: Most successful businesses have net profit margins that are around 10 percent or greater after paying the owner a high enough salary to live on. They also operate in a market where there is high customer demand and the possibility for their business to grow.
Examples of Net Profit Margin
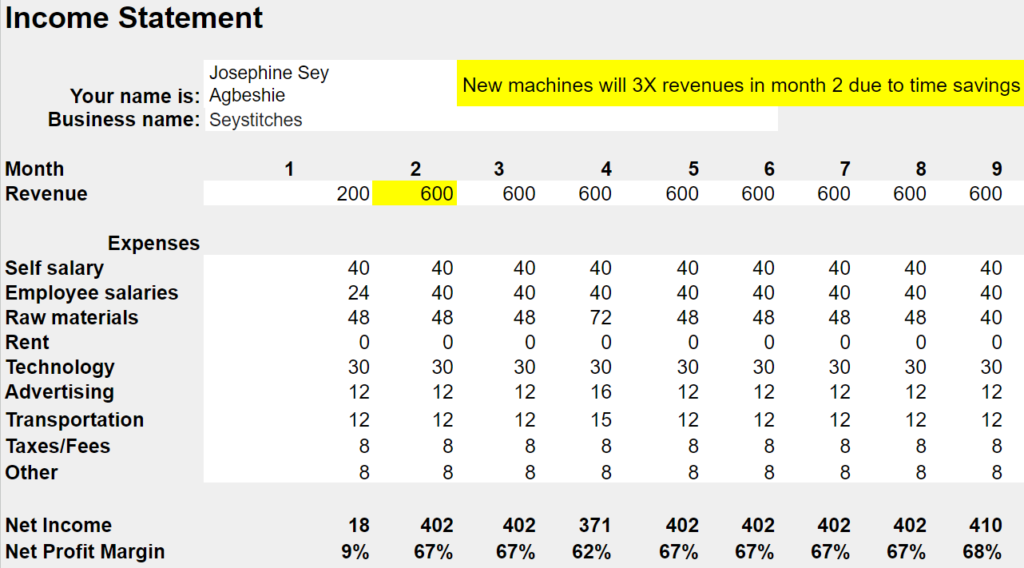
Read: Look at the income statement below for SeyStitches of Accra, Ghana. Her sponsor was impressed that she had calculated the increase in profit margins that would come from new, industrial sewing machines purchased with an Entrapov micro-loan. Notice that her net profit margin increased from 9% to 67% because the new machines could make her products (dresses) 3 times as fast without increasing expenses. Notice how she showed in her income statement that monthly revenues in month 2 would be 3 times as large as revenues in month 1 (from 200 to 600) because of the faster machines and time saved by not having to take her dresses to a rented knitting machine to finish them.
PRICE FOR MY SERVICE OR PRODUCT
Read: Your price must be high enough to pay for all costs and the profits you hope to make. However, you must set your price based on what you think customers will pay for your service or product. The price you charge depends on competitor prices and the quality of your service or product. You should work to increase the quality or perceived uniqueness of your service or product. This will allow you to charge a higher price than your competitors.
If the price customers are willing to pay would not make your business profitable enough, you should consider ways to lower your costs. Some of these ways include (1) purchasing in bulk at a reduced rate and (2) using multiple suppliers to gain better prices. If you are unable to lower your costs, you may need to choose a different business opportunity.
ACTIVITY (10 minutes)
Step 1: Divide into groups of three. Work together to calculate the net profit margin for your business opportunity for one month.

Discuss the following questions:
○ Does your net profit margin suggest that you’ve selected a business opportunity that can be successful?
○ If not, what can you change to increase your prices or reduce your costs?
Watch: Talking to Customers (below)
Homework Assignment:
Ⓐ I will have conversations with at least five potential customers. Go to where customers are buying the product you want to sell. Ask why they buy the product from this business. Ask how they would improve the product if they could. Ask how they feel about the product’s price. Then after speaking with 5 customers, come back to this page and answer the questions below to submit your homework assignment to Entrapov and your class facilitator.
